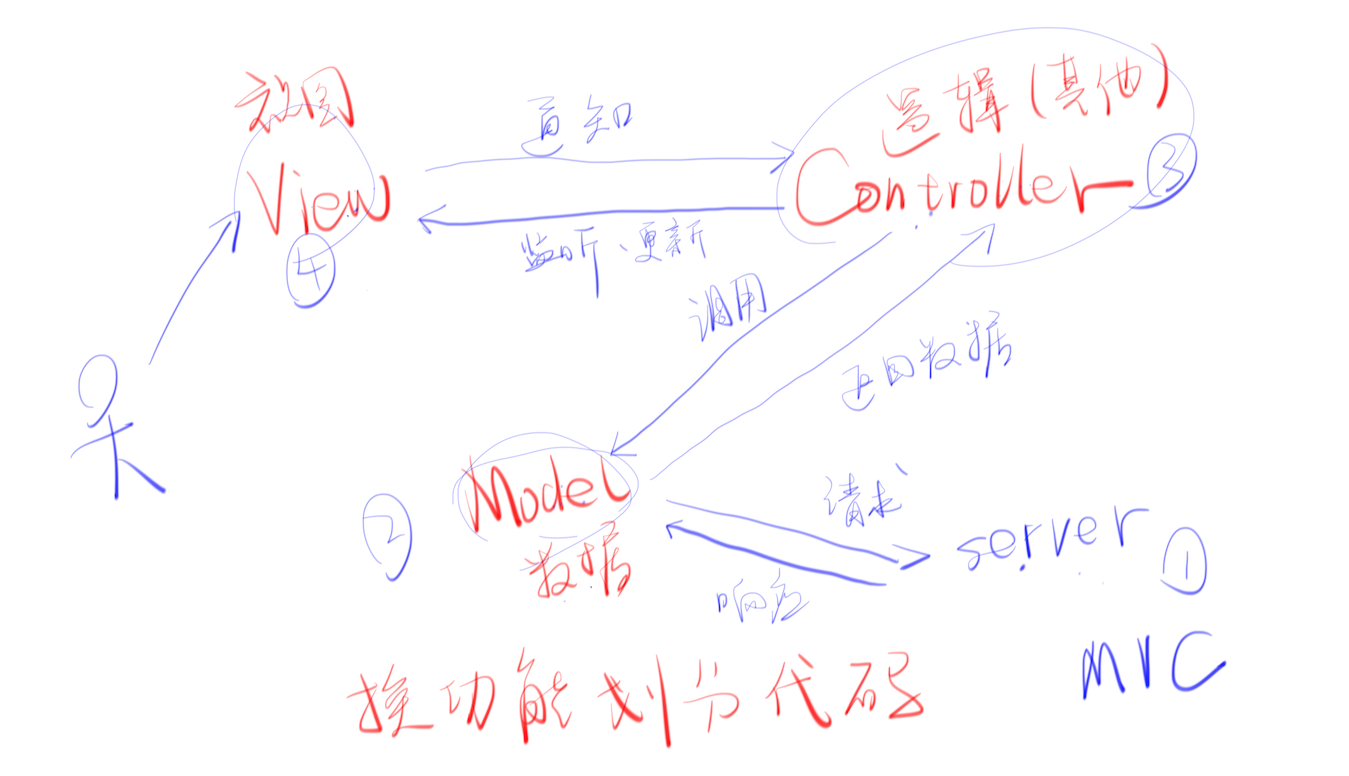
简易 MVC 实践
MVC = Model (操作数据)、View (表示视图)、Controller (控制器) 是代码组织形式,只是一种思想。就是把一坨代码转成 MVC 结构的代码。
功能转换为模块
模块对应的能看到的部分 HTML 指定给 view
操作 view 的逻辑指定为 controller,所以可以转换为函数 controller,controller(view)
var view = document.querySelector('#wrapper')
var controller = function(view) {
window.addEventListener('click', e => view.classList.add('class'))
}controller 作为对象,把 controller 函数作为这个对象的 init 函数,controller(view) 转换为 controller.init(view)
var view = document.querySelector('#wrapper')
var controller = {
view: null,
init: function(view) {
this.view = view
window.addEventListener('click', e => view.classList.add('class'))
}
}
controller.init(view)controller 对象下再加上一个 bindEvents 函数,也就是操作 view
var view = document.querySelector('#wrapper')
var controller = {
view: null,
init: function(view) {
this.view = view
this.bindEvents()
},
bindEvents: function() {
var view = this.view
window.addEventListener('click', e => view.classList.add('class'))
}
}
controller.init(view)bindEvents 只进行 bind 事件
var view = document.querySelector('#wrapper')
var controller = {
view: null,
init: function(view) {
this.view = view
this.bindEvents()
},
bindEvents: function() {
window.addEventListener('click', e => this.clickWrapper)
},
clickWrapper: function(e) {
this.view.classList.add('class')
}
}
controller.init(view)
整个代码都变得很有条理了:
- 一个 view;
- 一个 controller,
- controller.init(view),
- controller 里有一个 bindEvents,
- 以及在 controller 里定义操作 view 的函数
- 再到 bindEvents 里面执行这些操作 view 的函数们。
最后一个 Model 与数据库交互
var model = { |
Model 和服务器交互,Model 将得到的数据交给 Controller,Controller 把数据填入 View,并监听 View。用户操作 View,比如点击按钮,Controller 就会接受到点击时间,Controller 这时会去调用 Model,Model 会与服务器交互,得到数据后返回给 Controller,Controller 得到数据就去更新 View。
MVC :职责分明,模块清晰,代码简单!😄